How To Evaluate A Business Idea: Is It Worth Building?
Building Software during a startup boom is exciting, but many new ventures fail fast. Before you spend time or money, you need quick proof that your idea solves a real problem.
This guide gives you a simple framework you can run on a weekend or extend over a few weeks. You’ll use a seven-step checklist to decide whether to build, pivot, or drop your idea based on real evidence.
Start with three core questions:
✔
✔
✔
You’ll also see how a Minimum Viable Test (MVT) helps you validate demand before building a full MVP. The goal is not perfect prediction; it’s reducing risk quickly so you protect your time and budget.
📌
Highlights
-
✔Follow a seven-step checklist to evaluate your idea with real evidence.
-
✔Focus on customer pain, willingness to pay, and repeatable acquisition.
-
✔Use Minimum Viable Tests (MVTs) before investing in full product development.
-
✔Track CAC, LTV, conversion, and payback to judge viability.
Why Evaluating A Business Idea Is Harder Than You Think
Evaluating a new idea is rarely straightforward. Early feedback is often mixed, and many strong businesses looked weak at first.
Airbnb is a well-known Example: Early critics dismissed the idea, yet customer demand proved otherwise. This shows that early opinions are not final proof of success or failure.
Uncertainty In Prediction And The Investor Effect
Funding and support can change outcomes. Investors do more than predict success; they often help create it through resources and connections. Treat investor feedback as useful input, but not a final decision.
Sector Differences And What That Means For Testing
Different industries require different validation approaches. R&D-heavy sectors (pharma, hardware, energy) often need technical proof points and longer timelines. Software and mobile apps are easier to iterate, so predictability is lower, but experimentation is cheaper and faster.
For Example: Florida lifestyle or services app can often be validated quickly with local concierge pilots or partner demos, while an energy device would need lab validation and regulatory checks.
Practical Takeaway
Collect feedback from customers, operators, and mentors. Then run quick tests that produce measurable signals. Decisions should come from evidence, not opinions alone.
What Idea Validation Means And When You Should Do It
Spend days, not months, learning whether paying customers exist for your product. Idea Validation is the focused evidence-gathering that proves a target customer has a painful problem and will pay before you commit heavy resources or hire a development team.
Idea Validation vs. Business Planning
Planning records assumptions and builds a roadmap. Validation tests those assumptions quickly and tries to disprove them so you don’t spend time or money on the wrong bet. Run validation before you quit your job, start major development, sign a lease, or scale marketing spend.
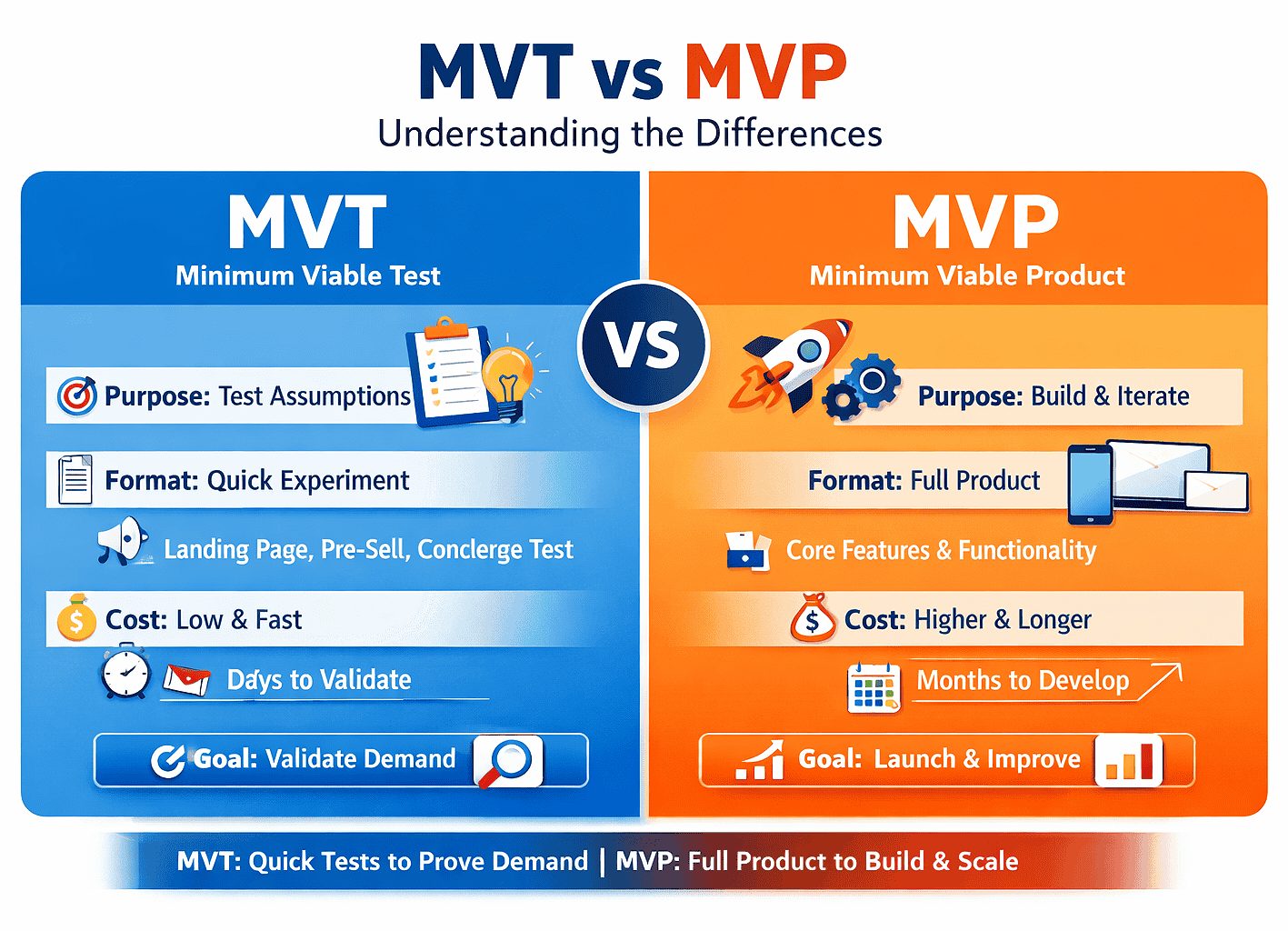
MVT vs MVP
Use a Minimum Viable Test (MVT) to answer your biggest risks first. An MVT is a low-cost experiment, such as a landing page, pre-sell, or manual delivery.
An MVP is a working product you release and improve over time.
Start with an MVT to confirm demand, pricing, and acquisition cost. Build an MVP only after those signals repeat.
How To Test A Business Idea — Quick MVT Examples For App & Saas Founders
Landing page + ads: Run targeted ads (Google, Facebook, LinkedIn) to a single-page value prop and an email + optional refundable deposit form. Measure CTR, conversion, and cost-per-signup to estimate CAC. For a Florida-focused SaaS, target local industry keywords and measure local signup rates.
Pre-sell: Offer a paid early-access or discounted subscription with a clear delivery timeline and refund policy. Ten paid commits in 30 days is a reasonable quick-pass threshold for many B2B tests that treat numbers as heuristics, not absolutes.
Concierge delivery: Manually deliver the service for a small set of customers, log the steps you’d automate later, and watch for repeat requests (≥3 repeats is a useful early signal).
Outcomes That Matter
Willingness to pay: Pre-orders, refundable deposits, or signed LOIs show real commitment.
Repeatability: Your acquisition and delivery process works reliably more than once.
Traction signals: Conversion rate, early retention, and referral activity.
If these signals appear consistently, move forward. If not, adjust your segment or offer and run another test.
Try this now: Launch A Landing Page With A 5–10 day ad run to validate search intent and early CAC.
See the MVT checklist later in this guide or use Webo 360 Solutions’ MVT support to design and run the test for you.
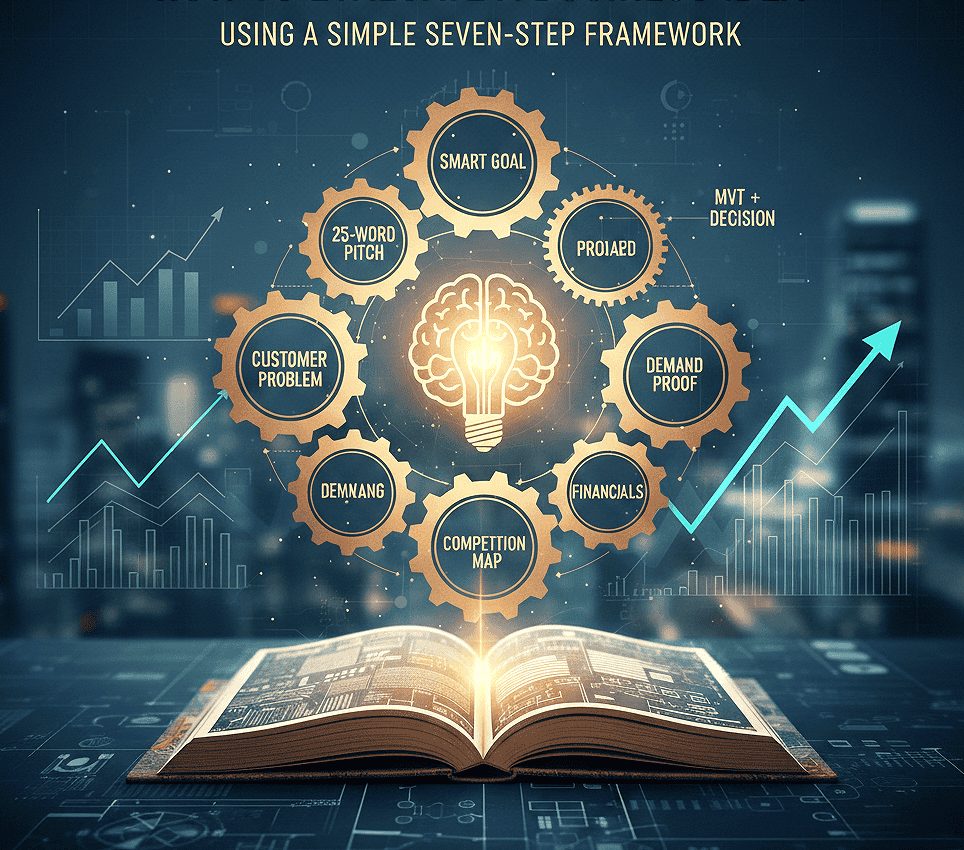
How To Evaluate A Business Idea Using A Simple Seven-Step Framework
Follow seven clear steps that produce concrete outputs and let you decide fast — a practical way to evaluate startup ideas for app and SaaS founders.
SMART goal + constraints: Write one sentence with your target income, timeline, and limits (budget, hours/week, legal).
Output: one clear success line.
Example: “Reach $6k MRR in 9 months from Florida SMBs with a $5k dev budget and 10 hours/week.” This gives a measurable north star for every test.
25-word pitch: Say who, the problem, the solution, and why now.
Output: one 25-word paragraph you can read aloud.
Sample for a Florida SaaS: “For Florida property managers who waste hours on scheduling, our app automates maintenance bookings and reduces admin time 50% — launch-ready with local pilots.”
Customer problem: List the exact user, their job, current workaround, and cost in time or money.
Output: one short customer profile.
Example: “Independent condo manager; manual spreadsheets; 6 hours/week; $500 monthly admin cost.”
Demand proof points: Run fast signals—search intent, waitlist, demo, pre-sell, partner intro.
Output: counts or signed commits.
How to evaluate a business idea: Prioritize signals that show willingness to pay (email+deposit, LOIs) and repeatable acquisition across channels.
Competition map: Name direct and indirect rivals and state your proposition (faster, cheaper, higher trust).
Output: A competitive table.
Example entry: Direct – legacy PMS; Indirect – spreadsheets; USP – “integrates with QuickBooks and offers white-glove onboarding.”
Financial analysis: Estimate pricing, gross margin, CAC, LTV, contribution margin, and payback.
Output: Unit economics with a pass/fail line.
Quick template: Price × gross margin = contribution per customer; CAC ÷ contribution = payback months. Use conservative assumptions for early evaluation.
MVT + decision: Run a minimum viable test with clear pass or fail thresholds. Decide in advance what counts as success, such as a 2% landing-page conversion or several paid pre-orders. After the test, choose one action: build, pivot, or stop and document your results.
Actionable way: Copy this checklist into notes and run one step per day (or batch them across a week). The goal is quick evidence, not perfection.
If you want a ready template, start your workable business idea checklist now, or Book A 30-Minute Webo 360 Solutions call to get a validation sprint scoped and a ready MVT plan.
Market Research For Idea Validation That Actually Finds Real Demand
Good market research separates guesses from real demand before you write code or sign leases. For app and SaaS founders, focused market research shows whether users truly need your product or service and whether you can reach them affordably.
Start with customer interviews that uncover a “must-solve” problem.
Ask four quick prompts: When the problem last happened, what you tried, what it cost, and what “solved” looks like. Record the exact language those words become your ad copy and landing-page headlines.
Use Search Intent, Forums, And Reviews
Scan high-intent queries and copy the words customers use. Use search intent and customer language to guide your research. Tools like Google Trends and Search Console help you find real demand signals.
Forums, reviews, and community discussions reveal common complaints and unmet needs. Mine Reddit, niche forums, LinkedIn groups, and reviews on G2, Yelp, and Amazon for repeated complaints and feature requests uncover unmet market needs and help with positioning.
Size The Potential Market And Sanity-Check Growth
Define your ICP (ideal customer profile), estimate reachable users in your first channels, and apply a realistic penetration rate for 12–24 months. For early-stage tests, focus on an addressable beachhead rather than TAM. Compare your numbers to industry growth trends to judge if the potential market and market share justify investment.
SWOT And PESTEL As Risk Filters
Use quick risk checks to spot legal, economic, or competitive threats early. Even a short review can reveal issues that might block growth later.
“Listen for urgency and budget ownership; willingness to pay beats polite praise every time.”
| Step | Signal | Quick threshold |
|---|---|---|
| Landing page | Conversion rate | ≥2% (rule of thumb) |
| Pre-sell / waitlist | Waitlist-to-signup rate | ~10% paid commits (heuristic) |
| Concierge test | Repeat requests | ≥3 repeats |
| Market sizing | Potential market estimate | Realistic early growth ≥10% yr (illustrative) |
Benchmarks to track: Landing page conversion, waitlist-to-signup, show-up rate for calls, and repeat purchase signals.
For Florida Founders: Add local channels, Meetup groups, chamber lists, industry Slack communities, and local LinkedIn outreach to quickly measure real demand in your region.
Practical checklist (market research for idea validation):
Interviews → search-intent keyword list → forum & review mining → ICP & market-sizing → run a small MVT.
If you want a worksheet, download the market research for idea validation template or request a short Web research audit to accelerate recognizing real market demand and answer “How To Know If The Idea Will Succeed.”
Competitors, Positioning, And Your Unique Selling Proposition
Before you commit to a product roadmap or hire an engineering team, map who your customers currently are or what they use instead. A clear competitor map shows direct rivals, indirect substitutes, and the practical gaps your proposition can exploit.
Find The Closest Alternatives In The Marketplace
List what customers use today: competitor products, spreadsheets, agencies, internal teams, or doing nothing. Separate direct competitors (same category) from indirect substitutes that solve the same job. This clarifies real competitive pressure and where you can win market share.
Define A Provable USP
Use this template:
For [customer], who [problem], your [product/service] delivers [measurable outcome] unlike [alternative] because [proof].
Proof might be speed metrics, verified ROI, exclusive channels, proprietary data, or regulatory advantage evidence that your customers and partners can verify.
Competitive Traps And Fixes
“Better service” is a weak proposition unless you can prove it. Watch for features that are easy to copy and offers that require a large behavior change.
Reduce friction, integrate with current workflows, offer done-for-you onboarding, or provide risk-reversal guarantees so customers can try without major disruption.
Use a 2×2 competitor map to visualize substitutes and identify white space — for example, map convenience vs cost and see where spreadsheets or agencies sit.
App/SaaS example (Florida): For Florida condo managers who need recurring maintenance scheduling, your SaaS automates bookings and reduces admin time by 50% — unlike spreadsheets, because it integrates with QuickBooks and provides white-glove onboarding.
That concrete proposition ties product benefits to measurable outcomes and reduces customer hesitation.
| Type | Example | Key insight |
|---|---|---|
| Direct | Legacy PMS | Same category, established feature set |
| Indirect | Spreadsheets/agencies | Substitutes with higher friction or cost |
| Other substitutes | DIY / in-house scripts | Low cost, high switching risk |
“If customers can return to old habits easily, your potential is limited unless you remove that friction.”
Ready to Act: Map your competitors using a simple table (direct, indirect, substitutes) and state your provable proposition for each target segment.
Download the competitor template in the Workable business idea checklist or request a quick positioning review from Webo 360 Solutions to refine your USP with measurable proof.
Financial Viability: Can This Business Idea Make Money And How Fast?
Run a quick money check that shows whether scaling will buy profit or only scale losses. This unit economics first approach tells you whether the business idea has the financial fundamentals to grow into a viable company.
Unit economics — plain definitions:
LTV = average revenue per customer × expected lifespan. CAC = total sales + marketing spend ÷ new customers. Contribution margin = price − variable cost per customer. Payback period = CAC ÷ monthly contribution per customer.
These simple formulas drive your go/no-go for scaling.
Cost Anatomy And Break-Even
List startup costs (legal, tooling, initial dev), fixed costs (salaries, hosting), and variable costs (COGS, fulfillment, payment fees). Sum them to estimate the monthly burn and one-time setup needs.
Break-even math (one-line): Break-even units = fixed costs ÷ contribution margin per unit. That tells you the sales volume needed and roughly how long to reach profitability.
Pricing Reality Checks
Compare willingness-to-pay signals (pre-sells, competitor pricing, interviews) against the price you need to hit CAC payback and margin targets. If the required price exceeds market willingness-to-pay, rethink the model or target a different segment with higher potential.
Services: Revenue is time-bound—price for hourly value and utilization. Unit economics depend heavily on the utilization rate.
Product or SaaS: Include COGS, returns, hosting, and support costs in your contribution margin calculation; subscription pricing changes payback math significantly.
Funding And Personal Risk
Bootstrapping, loans, or investors each change control, runway, and speed. Match funding to your risk boundary and resources. This is not financial advice; consult an accountant or advisor for tax or legal implications.
“Would you be willing to remortgage your house?”
| Metric | Quick threshold | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
| CAC | Lower — faster payback | Directly affects how quickly you recover acquisition spend |
| LTV | > 3× CAC (rule of thumb) | Indicates potential for scalable profitability in many SaaS models |
| Payback | Shorter — protects cash (months) | Short payback reduces runway pressure and funding needs |
Worked example (SaaS): Price = $30/month; average lifespan = 24 months → LTV = $720.
If the contribution margin is 60% → contribution = $18/month. If CAC = $150, payback = $150 ÷ $18 ≈ 8.3 months. Use this to judge if payback fits your runway and risk tolerance.
Actionable next step: Plug your assumptions into a unit-economics template (price, gross margin, CAC, churn) and run sensitivity scenarios for +/−20% changes in CAC and churn.
If you want a ready spreadsheet or a quick sanity check, use Webo’s unit-economics template or request a brief financial review to see whether the numbers support scaling and share potential with investors.
Minimum Viable Test Playbook: Practical Ways to Test A Business Idea
Run cheap experiments that answer the riskiest unknowns before you write code or hire staff. Use tests that produce clear CAC, conversion, and willingness-to-pay signals so you can decide whether your product or service is worth building.
Landing Page + Ads
Steps to set up: Create a single-page value prop, one call-to-action, and tracking (Google Analytics/GTM + pixel).
Run a 5–10 day ad test on Google, Facebook, or LinkedIn targeting your ICP. Measurement events include click-through rate, cost per signup, and cost per paid lead (use Stripe for pre-sells).
Expected timeline: 1–2 weeks to collect signal. Example: for a Florida hospitality app, run ads to an “early access + $20 refundable deposit” page to estimate CAC and conversion.
Pre-Sell And Concierge
Steps to set up: Craft a clear offer, set a refundable deposit or pre-order flow, and state delivery timing. Measurement events include the number of paid commits, refund requests, and manual delivery effort logged.
Expected timeline: 2–4 weeks for initial commits. For services, deliver manually (concierge), document steps to automate, and watch for repeat customers as proof of product-market fit.
Marketplace, Partners, Pilot
Steps to set up: Recruit suppliers or partners, run a small pilot through an existing channel, and measure conversion and retention.
Measurement events: Partner introductions, pilot uptake, and repeat transactions.
Expected timeline: 2–6 weeks, depending on partner cadence. Use local partners to boost early conversions and validate both supply and demand.
If tests pass, build an MVP that preserves the retention hooks you validated and measures LTV. If not, pivot segment, channel, or product and run the next minimum viable test (MVT).
These idea validation techniques are the fastest way to learn whether your ideas can scale or should be dropped.
Ready to launch an MVT? If you want a tested playbook, download the MVT playbook PDF or request Webo 360 Solutions to design and run the test for your Florida app or SaaS — we’ll estimate CAC, track conversion, and show you whether your idea is worth building.
Examples and Local Angles For High-Entrepreneurship U.S. Markets
Local tests give faster answers than national guesses.
Pick experiments that match each state’s strength, then measure problem clarity, demand proof, competitor reality, CAC/LTV, and run an MVT with clear pass/fail thresholds.
Florida: Validate service and lifestyle plays via partner pilots, deposits, and concierge runs. For example, test a Miami property-management SaaS by running concierge pilots with 5 local property managers, measuring repeat bookings, show-up rates, and local CAC. This quickly reveals whether the potential market and market share are realistic.
California: For product and software bets, run landing-page CAC tests and recruit beta users. Track retention as the core signal for long-term growth.
New York: Use dense demand to test premium pricing and short B2B sales cycles. Validate higher LTV with paid discovery pilots and enterprise pilots.
Texas: Focus on distribution and scaling. Pilot reseller deals and outbound channels; watch unit economics closely before growth spend.
Massachusetts: Lean on technical validation, IP checks, and expert review for R&D-heavy industries like biotech and energy.
Illinois: Run small paid pilots that test timing, reliability, and repeat purchase rates for logistics plays.
Washington: Target tech-forward customers and validate adoption with usage frequency and expansion signals.
| State | Primary test | Quick pass |
|---|---|---|
| Florida | Concierge pilot/partner pilot | ≥3 repeats/month; demonstrable local CAC |
| California | Landing page + beta | Retention >30% at 30 days |
| New York | B2B pilot | Paid pilot or deposit |
Florida Founders: Request a local pilot plan or download our state-test matrix to tailor experiments to your region and industry — a fast way to evaluate startup ideas and prove whether your idea is worth building.
Common Mistakes To Avoid When Evaluating A Business Idea
Mistakes in early assessment cost time and money faster than any feature build. You want clean, measurable signals, not compliments. Keep tests tight, document assumptions, and use evidence to decide whether to build, pivot, or stop.
Confusing Compliments With Demand
“That’s cool” is not a buying signal. Real demand shows up as calendar bookings, deposits, paid pilots, or signed commitments.
Quick fix: Require a paid pre-sell, refundable deposit, or scheduled demo with a time-bound commitment before you move forward.
Anecdote: A Florida founder paused development after 30 positive chats but zero deposits — the pause saved months of dev spend.
Skipping The 25-Word Clarity Test
If you can’t say who you serve and why it wins in one short line, your messaging will fail in ads and pilots.
Quick fix: Draft the 25-word pitch (step 2 in the framework) and test it in landing-page CTRs. Low CTRs signal your idea or positioning needs work.
Building An MVP Too Early
Skipping MVTs locks costs and assumptions. Run cheap tests first to measure CAC, willingness to pay, and retention before committing to an MVP build.
Quick fix: Run a landing page, pre-sell, or concierge pilot (see the MVT playbook) and only build if signals meet your pass/fail thresholds.
Ignoring Indirect Competitors
Customers revert to substitutes when your offering requires a big behavior change.
Quick fix: Map direct and indirect alternatives and state your provable advantage. If switching is easy, your market share potential will be limited unless you remove friction.
Waiting On CAC And LTV
Estimating acquisition and lifetime value late can hide unscalable growth. Measure these metrics early in pilots to inform pricing and go-to-market decisions.
Quick fix: Track cost per lead, conversion, and projected LTV from your first paid users and use conservative assumptions in analysis.
Narrow Feedback And Founder Fit
Don’t rely only on friends, a single mentor, or a narrow customer set. Diverse feedback exposes operational and go-to-market risks early.
Quick fix: Interview prospects across five segments, set a personal resource cap (time, money), and decide in a fixed window whether to continue.
| Mistake | Signal it’s happening | Quick test | Decision rule |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compliments trap | No deposits or bookings | Offer paid pilot | Pause if paid commits = 0 |
| Unclear pitch | Low ad CTR | 25-word pitch test | Revise if CTR <2% |
| Skipping MVT | High dev cost, low learning | Landing page or concierge | Delay the build until the CAC is proven |
| Narrow feedback | Conflicting signals later | Interview 20 prospects | Stop if no repeat requests |
Need a second opinion?
Request A Short Webo 360 Solutions review to run your idea validation process and apply proven idea validation techniques so you can know whether the idea will succeed or whether the idea is worth building.
How Webo 360 Solutions Can Help You Evaluate Your Business Idea
Webo 360 Solutions helps
Software Developers and tech entrepreneurs who need fast, evidence-based answers about whether a new app or SaaS business idea is worth building. We focus on practical idea validation techniques and short validation sprints that move you from hypothesis to decision, not long reports.
What We Offer
-
✔Idea validation guidance: One-on-one coaching to run the idea validation process, refine your 25-word pitch and SMART goal, and set pass/fail lines so you make clear decisions quickly.
-
✔Market research and analysis: Targeted market research for idea validation — search intent audits, ICP sizing, competitor mapping, and local Florida channel checks to help with recognizing real market demand.
-
✔Minimum Viable Test (MVT) support: We design and run minimum viable tests (MVTs) such as landing pages, app-store pre-launch pages, gated betas, ad campaigns, pre-sell funnels, and concierge deliveries, and we track CAC, conversion, and payback for you.
-
✔Workable business idea checklists: Ready-to-use templates and downloadable checklists (25-word pitch, unit-economics model, workable business idea checklist) so you can run the validation process consistently.
How We Work With You
We run outcome-focused sprints: a 5–7 day rapid validation sprint for a quick MVT or a 2–4 week deep validation when you need market research and pilot campaigns.
Deliverables are practical — a validated decision (build, pivot, or drop), a prioritized test plan, and an MVT ready to launch. We can also run pilot campaigns to measure CAC and early conversion on your behalf.
Ready to test? Schedule A Free 30-Minute Discovery Call With Webo 360 Solutions to scope an MVT for your Florida app or SaaS idea, or download our workable business idea checklist to start running idea validation techniques today.
If you’re wondering how to test a business idea or how to know if the idea will succeed, we can design the test and interpret the results with you.
Final Thoughts
Make a disciplined finish: Document your assumptions, set clear pass/fail lines, and pick the next action within a fixed window. You cannot predict success perfectly, but you can cut uncertainty fast with focused tests, concise analysis, and objective gates that protect your time and money.
Quick checklist: Write a SMART goal, craft the 25-word pitch, map the customer and problem, gather demand proof, map competitors, run unit economics analysis, then run an MVT and decide.
Prioritize the riskiest unknown demand, pricing, acquisition, or delivery, and prove willingness to pay before building an MVP. Track CAC, LTV, contribution margin, payback, conversion rate, and retention as your truth metrics so you can evaluate startup ideas with evidence, not hope.
Next Actions: Write your 25-word pitch today, book 10 customer interviews this week, and launch one MVT within 14 days. Document results and make a timely build, pivot, or drop decision based on the evidence you collect.
Frequently Asked Questions.
What key signals show an idea is worth building?
When should you run a Minimum Viable Test instead of building an MVP?
Which testing methods prove the real demand fastest?
How do you pressure-test financial viability early?
How do you size the market without overcommitting to big TAM numbers?
Who should you involve in early validation besides customers?
Final note (Florida app & SaaS founders): If you want an expert review of your idea, a ready MVT plan, or help running market research for idea validation, explore Webo 360 Solutions’ Validation Services or book a free discovery call to scope a short validation sprint. We’ll help you evaluate your business idea and decide whether your idea is worth building.